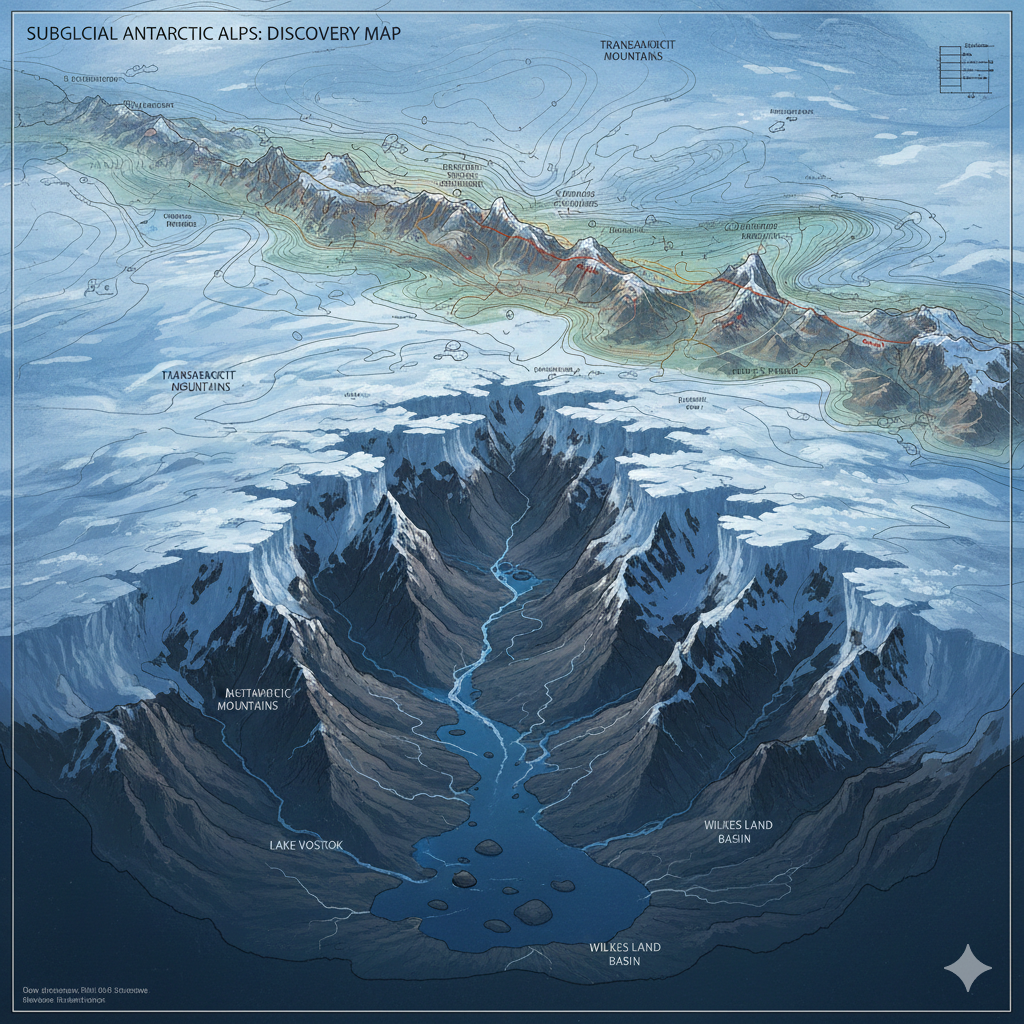
Scientists Create Historic Map Using Satellite Data; To Aid Predictions of Ice Melt and Sea Level Rise
The several-kilometer-thick ice sheet of Antarctica has long acted as a mysterious shroud, hiding the true face of an entire continent. Now, scientists have presented the first detailed and startling map of that ‘lost continent’ buried beneath the ice. This map reveals a stunning alpine landscape of high mountains, deep valleys, and vast plains.
This historic mapping was made possible using an innovative technique called ‘Ice Flow Perturbation Analysis’ (IFPA). An international team of researchers analyzed data from satellites to determine that subtle undulations on the ice surface act like a ‘shadow’ of the underlying ground structure. This method has helped fill the vast gaps present in traditional radar surveys.
Key Highlights:
- Extremely Diverse Terrain: The map does not show just a flat, barren land. Instead, it includes rugged mountainous regions, valleys as deep and wide as the US Grand Canyon, and broad basins. These deep troughs were carved over millennia by fast-flowing rivers of ice (ice streams).
- Less Known Than Mars: Ironically, scientists know more about the surface of Mars than they do about the ground beneath Antarctica’s ice. This map is a giant leap towards understanding one of the last unexplored corners of our own planet.
- Crucial for Climate Forecasts: This discovery is not just about curiosity. This map will prove to be a critical tool for predicting how Antarctica’s ice will melt in the future and how it will impact global sea levels. The shape of the bedrock directly influences the speed and stability of ice flow.
- Identification of New Regions: The study also names new geographic features like the ‘Golicyna Subglacial Regions’ and ‘Subglacial Highlands’.
What Do Scientists Say?
The lead researcher stated, “This landscape turned out to be far more diverse and complex than our previous estimates. It’s as if we have discovered a new continent on Earth that had been buried under ice for eons.”
Although this technique is revolutionary, it has some limitations. It cannot fully capture structures smaller than 2 kilometers or wider than 30 kilometers. Nevertheless, this study is considered a decisive step towards understanding Antarctica’s fate in an era of climate change.
Hindi Version News
बर्फ के नीचे छिपा ‘लुप्त महाद्वीप’: नए नक्शे ने उजागर किया अंटार्कटिका का आश्चर्यजनक अल्पाइन परिदृश्य
वैज्ञानिकों ने उपग्रह डेटा की मदद से बनाया ऐतिहासिक मानचित्र; बर्फ पिघलने और समुद्र स्तर की भविष्यवाणियों में मिलेगी मदद
अंटार्कटिका की कई किलोमीटर मोटी बर्फ की चादर हमेशा से एक रहस्यमय आवरण का काम करती रही है, जिसने एक पूरे महाद्वीप के वास्तविक स्वरूप को छिपा रखा है। अब, वैज्ञानिकों ने पहली बार उस ‘लुप्त महाद्वीप’ का एक विस्तृत और चौंकाने वाला नक्शा पेश किया है, जो बर्फ के नीचे दबा हुआ है। यह नक्शा ऊँचे पहाड़ों, गहरी घाटियों और विशाल मैदानों वाले एक अद्भुत अल्पाइन परिदृश्य को उजागर करता है।
इस ऐतिहासिक मानचित्रण को ‘आइस फ्लो परटर्बेशन एनालिसिस’ (IFPA) नामक एक नवीन तकनीक के जरिए संभव बनाया गया है। शोधकर्ताओं की एक अंतरराष्ट्रीय टीम ने उपग्रहों से प्राप्त आंकड़ों का विश्लेषण कर यह पता लगाया कि बर्फ की सतह पर दिखने वाले सूक्ष्म उतार-चढ़ाव नीचे की जमीनी संरचना की ‘छाया’ की तरह हैं। इस विधि ने पारंपरिक रडार सर्वेक्षणों में मौजूद विशाल खाली जगहों को भरने का काम किया है।
मुख्य बिंदे:
- अत्यंत विविध भूभाग: नक्शा केवल एक समतल, बंजर जमीन का चित्र नहीं दिखाता। बल्कि, इसमें ऊबड़-खाबड़ पहाड़ी क्षेत्र, अमेरिका के ग्रैंड कैनयन जितनी गहरी और चौड़ी घाटियाँ, और चौड़े बेसिन शामिल हैं। इन गहरी खाइयों का निर्माण तेज गति से बहने वाली बर्फ की नदियों (आइस स्ट्रीम) ने हजारों सालों में किया है।
- मंगल ग्रह से भी कम ज्ञात: एक विडंबना यह है कि वैज्ञानिकों को मंगल ग्रह की सतह के बारे में अंटार्कटिका की बर्फ के नीचे की जमीन से कहीं अधिक जानकारी है। यह नक्शा हमारे अपने ग्रह के अंतिम अनछुए कोनों में से एक को समझने की दिशा में एक बड़ी छलांग है।
- जलवायु अनुमानों के लिए महत्वपूर्ण: यह खोज सिर्फ जिज्ञासा भर नहीं है। यह नक्शा भविष्य में अंटार्कटिका की बर्फ कैसे पिघलेगी और वैश्विक समुद्र स्तर को कैसे प्रभावित करेगी, इसका पूर्वानुमान लगाने के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण उपकरण साबित होगा। नीचे की जमीन की आकृति बर्फ के प्रवाह की गति और स्थिरता को सीधे प्रभावित करती है।
- नए क्षेत्रों की पहचान: अध्ययन में ‘गोलित्सिना सबग्लेशियल क्षेत्र’ और ‘सबग्लेशियल हाइलैंड्स’ जैसे नए भौगोलिक क्षेत्रों का भी उल्लेख किया गया है।
वैज्ञानिकों का क्या कहना है?
शोध दल के प्रमुख ने बताया, “यह परिदृश्य हमारे पिछले अनुमानों से कहीं अधिक विविधतापूर्ण और जटिल निकला है। यह ऐसा है मानो हमने पृथ्वी पर एक नया महाद्वीप खोज लिया हो, जो सदियों से बर्फ के नीचे दबा था।”
हालाँकि यह तकनीक क्रांतिकारी है, लेकिन इसकी कुछ सीमाएँ भी हैं। यह 2 किलोमीटर से छोटी या 30 किलोमीटर से अधिक चौड़ी संरचनाओं को पूरी तरह पकड़ नहीं पाती। फिर भी, यह अध्ययन जलवायु परिवर्तन के युग में अंटार्कटिका की नियति को समझने की दिशा में एक निर्णायक कदम माना जा रहा है।